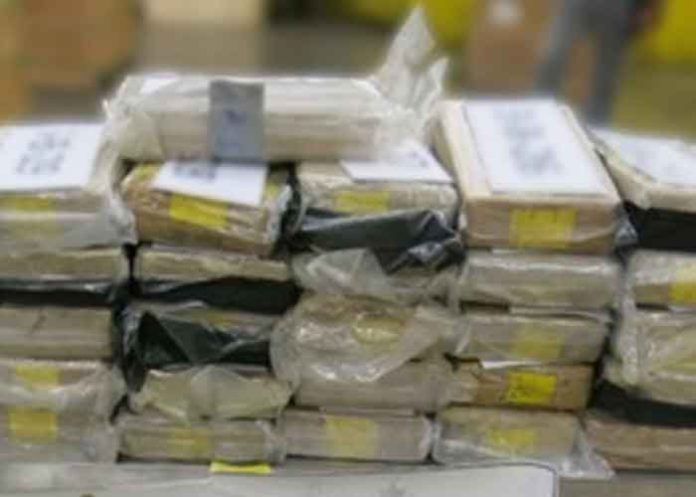
India’s diverse socio-cultural fabric and varying regional dynamics have resulted in a significant variation in illegal drug consumption across its states. The factors influencing these differences include geographic location, economic conditions, law enforcement practices, and the availability of narcotic substances.
Punjab: A Growing Epidemi
Punjab, particularly in rural areas, has been widely regarded as the epicenter of India’s drug abuse problem. The state’s proximity to the international border with Pakistan facilitates the trafficking of heroin and other narcotics.
Studies estimate that a large proportion of Punjab’s youth is addicted to drugs, which has led to a serious public health crisis.
The drug problem is so severe that it is now seen as an epidemic, with heroin being the most abused substance. Although the government has launched several programs to combat the crisis, the issue continues to escalate, and the registration of drug-related cases remains high.
Himachal Pradesh: The Role of Cannabis
In Himachal Pradesh, illegal drug use is closely tied to the cultivation of cannabis and opium poppies, especially in rural regions. Cannabis, or marijuana, is the most commonly abused substance, though synthetic drugs and heroin have also been reported.
The state’s location along drug-trafficking routes from neighboring countries like Nepal and Afghanistan exacerbates the issue. Additionally, a combination of socio-economic factors, limited job opportunities, and lack of awareness contributes to drug abuse, especially among the youth.
Goa: Drugs in the Tourism Industry
Goa, known for its tourism-driven economy, faces a unique challenge when it comes to illegal drug use. The state’s popularity among international tourists has fueled the demand for recreational drugs, such as MDMA (ecstasy), cocaine, and marijuana.
The party culture in popular tourist destinations, such as the beaches of Anjuna and Baga, has made Goa a hotspot for drug consumption. Despite efforts by law enforcement to control the supply and use of narcotics, the prevalence of drug abuse remains a persistent issue, especially during the tourist season.
Northeastern States: The Heroin Hotspot
The northeastern states of India, particularly Manipur, Nagaland, and Mizoram, have the highest prevalence of heroin use. These states share borders with Myanmar, a significant producer of opium and heroin. As a result, heroin trafficking into these regions is rampant, and many people, particularly youth, fall prey to addiction.
In Manipur, it has been reported that as many as 50% of the youth are addicted to drugs, making it one of the most affected regions. The insurgency and instability in these areas have further hindered efforts to tackle the drug menace.
Delhi and Haryana: Urban Drug Abuse
In the National Capital Region (NCR), comprising Delhi and parts of Haryana, illegal drug consumption is a significant concern, especially in urban areas. Heroin, marijuana, and synthetic drugs like methamphetamine are prevalent.
The high population density, migration patterns, and socio-economic disparity contribute to drug abuse in these regions. Though the law enforcement agencies are active in fighting drug abuse, the rising demand for drugs coupled with drug trafficking networks complicates enforcement efforts.
Maharashtra: The Gateway for Drug Trafficking
Mumbai, the financial capital of India, faces challenges with the consumption of illegal drugs, including cocaine, heroin, and synthetic drugs. The city’s high international connectivity, combined with its position as a major transit point for drug trafficking, has made it a hotspot for illegal drug consumption.
Although the state government and law enforcement agencies have been proactive in combating drug trafficking, the extensive network of drug peddlers and consumer demand remain significant hurdles.

Registration of Drug-Related Cases: Challenges and Trends
While the consumption of illegal drugs is widespread across India, the registration and prosecution of drug-related cases often face numerous challenges:
1. Underreporting and Stigma
In many states, particularly rural and conservative regions, there is a significant stigma attached to drug abuse. Individuals who struggle with addiction often do not come forward due to fear of social ostracization or legal consequences. Consequently, drug-related cases remain underreported, and law enforcement agencies may not have accurate data regarding the extent of drug consumption and trafficking.
2. Lack of Infrastructure and Resources
The lack of adequate infrastructure in several states impedes the effective registration and resolution of drug-related cases. In regions with insufficient resources, including a shortage of trained police officers and drug testing labs, it becomes difficult to effectively prosecute drug offenders. Additionally, limi