Moscow, September 17, 2024 (Yes Punjab News)
Russia is facing a serious demographic crisis, with its birth rate at its lowest point in 25 years. In response to this issue, Russian President Vladimir Putin has reportedly encouraged citizens to make procreation a priority, even suggesting that Russians use their lunch and coffee breaks at work to conceive children.
This unusual recommendation has sparked discussions about how far the Russian government is willing to go to address the country’s population decline.
Russia’s Birth Rate Crisis: A National Emergency
Russia’s birth rate has been in decline for several years, and the current fertility rate stands at 1.5 children per woman, well below the 2.1 children per woman needed for population stability. The situation has worsened due to various factors, including the ongoing war with Ukraine, which has caused the exodus of more than a million young Russians.
Putin’s Suggestion: Making Procreation a Workplace Activity
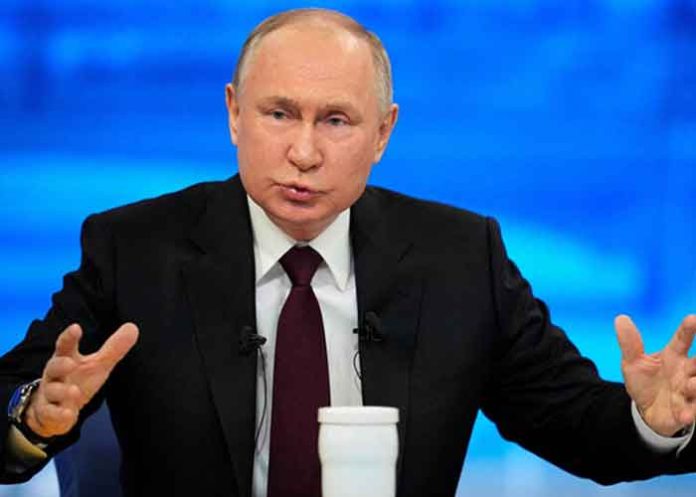
In a report by *Metro*, Russian President Vladimir Putin allegedly suggested that Russians should not let their work schedules prevent them from contributing to the country’s birth rate. According to the report, Putin advised that couples could use their lunch and coffee breaks to have sex and, thus, help boost the population.
Russian Health Minister’s Support for Workplace Procreation
Russian Health Minister Dr. Yevgeny Shestopalov has echoed Putin’s sentiments, urging citizens not to use their busy work schedules as an excuse for not having children. “Being very busy at work is not a valid reason, but a lame excuse. You can engage in procreation during breaks, because life flies by too quickly,” Shestopalov reportedly said.
When asked about the feasibility of these suggestions, particularly for individuals working long hours, Shestopalov reiterated the importance of taking advantage of break times. “Make babies during break times,” he added.
Government Initiatives to Boost the Birth Rate
In addition to Putin’s workplace suggestion, the Kremlin has introduced several other measures to address Russia’s declining birth rate. These measures aim to encourage families to have more children and focus on improving reproductive health for women of childbearing age.
Free Fertility Screenings for Women
In Moscow, women between the ages of 18 and 40 are being offered free fertility screenings. These screenings are designed to assess their reproductive health and potential, making it easier for women to understand their fertility status and plan for family expansion.
Financial Incentives for Young Mothers
In the Chelyabinsk region of Russia, authorities have introduced a financial incentive to encourage young women to have children. Women under the age of 24 are being offered a payment of 1.02 lakh rubles (approximately Rs 9.40 lakh) upon the birth of their first child. This financial aid is intended to help alleviate the costs associated with raising a child and motivate women to start families earlier.
Restricting Access to Abortion
Russia has also been tightening its laws around abortion access. Public figures and religious leaders in Russia have been advocating for restrictions, arguing that a woman’s primary responsibility is to bear and raise children. By limiting access to abortion, the government aims to reduce the number of terminated pregnancies and increase the overall birth rate.
Increasing Divorce Fees to Promote Family Stability
Another measure introduced by the Kremlin to combat the declining birth rate is increasing divorce fees. The government believes that making it more expensive to dissolve marriages will encourage couples to stay together, thereby creating more stable family environments conducive to having children.
A Decline in Births: The Numbers Tell the Story
Recent statistics paint a grim picture of Russia’s demographic situation. The country recorded its lowest birth rate in 25 years during the first half of 2024. In June alone, the number of births fell below 100,000 for the first time in modern history. Between January and June 2024, Russia saw the birth of 599,600 children, 16,000 fewer than during the same period in 2023.
Kremlin’s Response to the Birth Rate Decline
The Kremlin has expressed alarm over the country’s falling birth rate. Kremlin spokesperson Dmitry Peskov called the situation “catastrophic for the future of the nation” in a statement made in July. He highlighted that Russia’s current birth rate of 1.4 children per woman is comparable to other countries facing similar population challenges, such as Japan and various European nations.
Global Comparisons: Russia’s Birth Rate in Context
Russia’s declining birth rate mirrors a broader trend seen in many industrialized countries. Nations like Japan, Italy, and Germany have also experienced falling birth rates, leading to aging populations and shrinking workforces. However, Russia’s demographic decline is exacerbated by additional factors such as emigration, the war with Ukraine, and economic instability, making the situation particularly dire.
The Impact of War on Russia’s Demographics
The ongoing war with Ukraine has had a significant impact on Russia’s population. Over one million, mostly young Russians, have left the country, further straining the birth rate. Many of those who left are of prime reproductive age, which compounds the problem of a declining fertility rate. This exodus has created a demographic void that is unlikely to be filled in the near future.
Can Putin’s Unconventional Solution Work?
While Putin’s suggestion to have sex during work breaks has sparked global headlines, it remains to be seen whether such unconventional advice will have any real impact on the birth rate. Critics argue that tackling Russia’s population crisis will require more substantive solutions, such as improving healthcare, providing better support for families, and addressing the economic factors that discourage people from having children.
What’s Next for Russia’s Population?
As Russia grapples with its declining birth rate, the government will likely continue to introduce policies aimed at boosting the population. Whether these efforts will be successful remains uncertain. For now, Russia’s demographic future hangs in the balance, with the potential for long-term consequences if the birth rate does not improve.
Russia’s Demographic crisis a complex issue
Russia’s demographic crisis is a complex issue driven by multiple factors, including political, social, and economic challenges. While Putin’s advice to engage in procreation during work breaks has garnered attention, it’s clear that the nation will need a more comprehensive approach to address its population decline.
Financial incentives, fertility screenings, and restrictive policies around divorce and abortion are just some of the methods being used to reverse the trend. However, only time will tell if these efforts will be enough to stabilize Russia’s population.
FAQs
1. What is Russia’s current birth rate?
Russia’s current fertility rate stands at approximately 1.5 children per woman, which is below the 2.1 children needed to maintain population stability.
2. Why is Russia’s birth rate declining?
Several factors contribute to the decline, including economic instability, the ongoing war with Ukraine, and the emigration of young Russians.
3. What measures has the Russian government taken to boost the birth rate?
The government has introduced financial incentives for young mothers, free fertility screenings, and stricter abortion and divorce laws to encourage family growth.
4. What did Putin suggest to address the declining birth rate?
Putin allegedly encouraged Russians to use their lunch and coffee breaks at work for procreation to help boost the country’s birth rate.
5. How has the war with Ukraine affected Russia’s population?
The war has led to the emigration of over a million young Russians, further contributing to the country’s declining birth rate and demographic crisis.